Crohn's Disease Treatment
Crohn's Disease Treatment
The aims of treatment for Crohn's disease are to control inflammation, relieve symptoms, make sure your child is growing well and has the vitamins and minerals they need. Some tamariki (children) may need to see a dietitian as part of their treatment.
Key points about Crohn's disease treatment
- treatment options depend on how severe your child's Crohn's disease is
- treatment for tamariki with Crohn's disease may include medicines
- talk to your doctor about your child's medicines and make sure you know the names and doses of the medicines, the side effects and why your child is taking them
- with effective treatment, it is possible to manage your child's symptoms and prevent flare-ups
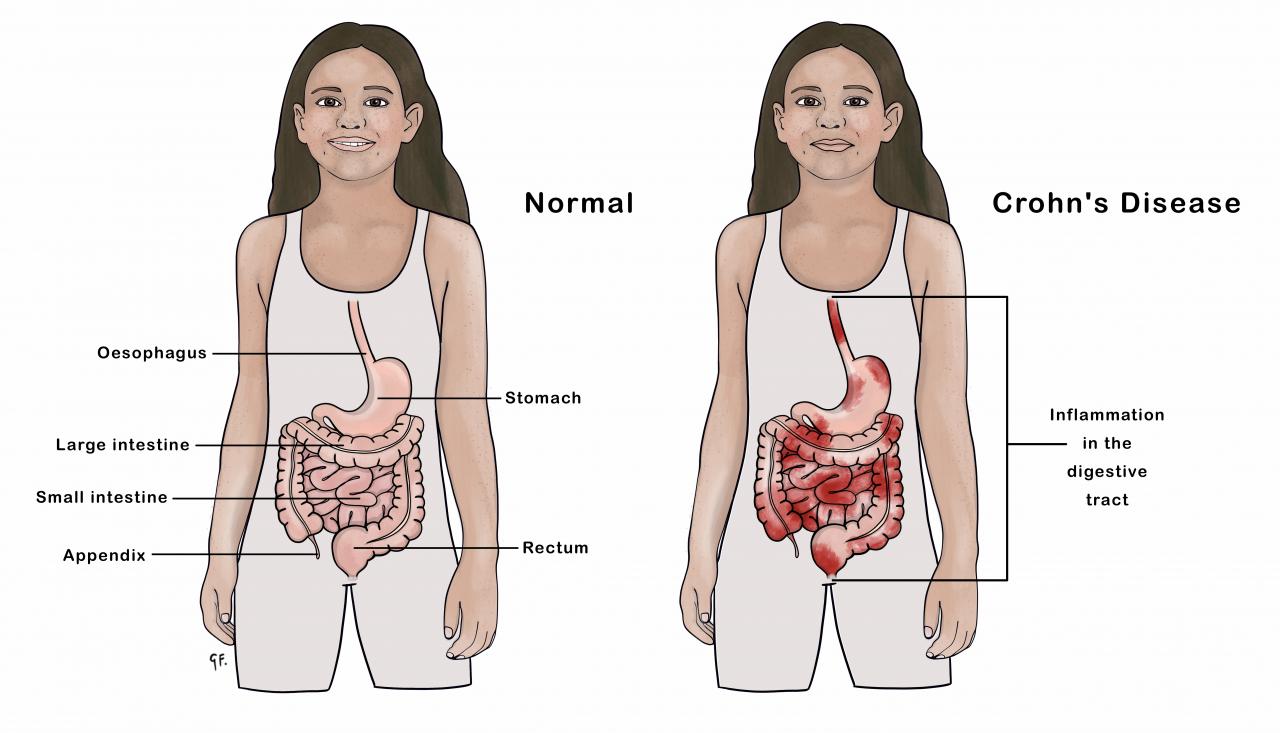
Crohn's disease is one type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). See the KidsHealth page on IBD.
What are the treatment options for my child with Crohn's disease?
Treatment aims
The aims of treatment for Crohn's disease are to control inflammation, relieve symptoms, make sure your child is growing well and has the vitamins and minerals they need. Some tamariki may need to see a dietitian as part of their treatment.
Treatment options
Treatment options depend on how severe your child's Crohn's disease is. Your child's paediatrician or other specialist will talk with you and your child about the best treatment.
With effective treatment, it is possible to manage your child's symptoms and prevent flare-ups, though it may take some time to find the best treatment for your child.
Will my child with Crohn's disease need exclusive enteral nutrition?
Exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN) is a treatment for Crohn's disease that involves drinking a formula for a specific period, instead of drinking and eating usual food. EEN uses a specifically balanced formula that will meet all of your child's daily nutritional needs. Using EEN will allow the bowel to heal and return to its healthy normal state, and should help your child regain weight they have lost because of their condition. Often tamariki have EEN when they first receive a Crohn's disease diagnosis. They may also have EEN if they have a relapse.
EEN works as well as medicines but has no side effects.
How long will my child need exclusive enteral nutrition?
Usually, tamariki have EEN for 8 weeks. Some tamariki will continue to drink a small volume of EEN for longer. Your child's dietitian will tell you how much of the formula you will need to give.
How will my child take exclusive enteral nutrition?
EEN comes in several flavours. Your child may have it by mouth (orally) or by a flexible tube through the nose and into the stomach (nasogastric tube).
See KidsHealth's information on tube feeding.
When your child is taking EEN, they need to drink extra water but no other food or drink.
Storing EEN
You can safely store EEN at room temperature, but it tastes better when it is cold. You can freeze EEN so the servings are still cold when your child has it at school. Your child can also have EEN half frozen or completely frozen.
When can my child have regular food and drink again?
After 8 weeks, you can start giving normal food and drinks to your child while gradually reducing the EEN. It's a good idea to start with foods that are low in fat, fibre and lactose with the support of a paediatric dietitian.
How can medicines help my child with Crohn's disease?
The aims of treatment with medicines
Treatment for tamariki with Crohn's disease may include medicines to:
- stop or control the inflammation
- stop the disease from getting worse, or keep your child free from symptoms
- prevent the immune system from attacking the body and causing the inflammation - your child may have some of these medicines by injection or infusion in hospital
- control pain
- provide the body with missing vitamins and minerals
Being informed about your child's medicines
Talk to your doctor about your child's medicines. Know the names and doses of the medicines, the side effects and why your child is taking them.
Alternative medicines
Your friends and family may suggest trying alternative medicines or treatment. Please discuss these with your doctor first, as some therapies can be harmful or may interact with your child's current medicines.
What medicines might my child with Crohn's disease need?
Children with Crohn's disease will often take more than one medicine together.
Aminosalicylates
These are often a treatment option for tamariki with mild to moderate symptoms. Examples include mesalazine, which your child may take as tablets, capsules or granules.
Steroids
These are for treatment of sudden flare-ups. These are not usually for long-term use. Examples include budesonide, prednisone and methylprednisone which your child may take as tablets, capsules, liquid or receive directly into a vein (intravenously).
Immunosuppressants
Most tamariki with Crohn's disease will receive azathioprine. This is a medicine to suppress the immune system.
Biologics
Biologic medicines work on controlling your immune system. They target specific proteins or pathways that cause inflammation and damage.
There are a number of biologic medicines. Each targets the inflammation in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) in different ways.
TNF inhibitors
TNF stands for tumour necrosis factor. It is one of the causes of inflammation in Crohn's disease.
TNF inhibitors are for tamariki who either:
- have severe Crohn's disease or
- have symptoms which don't improve when they take other medicines
Tamariki who have a fistula may also need to take TNF inhibitors.
Examples of TNF inhibitors are:
- infliximab
- adalimumab
Your child will have TNF inhibitors by injection.
Ustekinumab
Ustekinumab is a medicine that works by blocking another natural inflammatory substance in your body. This medicine helps to decrease inflammation in the gut, which eases symptoms. This may slow or stop damage from Crohn's diseasse.
If tamariki with severe Crohn's disease do not respond to treatment with TNF inhibitors, they may receive treatment with Ustekinumab.
Tamariki have this medicine by an injection under the skin.
Vedolizumab
Vedolizumab is another medicine for tamariki with severe Crohn's disease. This medicine binds to a compound on white blood cells. This leads to less white cell activity which reduces inflammation in the bowel.
Tamariki have this medicine as a drip (an infusion) into a vein.
Vitamins and minerals
Crohn's disease can cause problems with absorption of vitamins and minerals so some tamariki will need vitamins and mineral supplements. These are likely to include iron and vitamin D. They might also include vitamin B12, folate, magnesium and calcium.
Can a low FODMAP diet help my child with Crohn's disease?
A low FODMAP diet (a diet that avoids certain sugars) does not treat Crohn's disease. Studies show that no particular food is useful in treating Crohn's disease. A low FODMAP diet can be useful in treating irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). But, IBS is not the same as Crohn's disease and the treatments are very different. Some tamariki with Crohn's disease may also have IBS. It is important to talk with your child's doctor and dietitian before making any significant changes to your child's diet.
Will my child with Crohn's disease need surgery?
Some tamariki with Crohn's disease may need surgery if medicines don't work well enough. Your child's doctor will talk to you about this, if necessary.
This page last reviewed 22 May 2023.
Do you have any feedback for KidsHealth?
If you have any feedback about the KidsHealth website, or have a suggestion for new content, please get in touch with us.
Email us now